路由模式及降级处理
vue-router 默认是 hash 模式 , 即使用 URL 的 hash 来模拟一个完整的 URL ,于是当 URL 改变时,页面不会重新加载。
vue-router 还支持 history 模式,这种模式充分利用了 history.pushState 来完成 URL 跳转。
在不支持 history.pushState 的浏览器 , 会自动会退到 hash 模式。
TIP
是否回退可以通过 fallback 配置项来控制,默认值为 true
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'history', // history 或 hash
routes: [...]
});
详细使用可参看文档: HTML5 History 模式
根据 mode 确定类型
首先看下 VueRouter 的构造方法 , 文件位置 src/index.js
import { HashHistory } from './history/hash'
import { HTML5History } from './history/html5'
import { AbstractHistory } from './history/abstract'
// ... more
constructor(options: RouterOptions = {}) {
// ... more
// 默认hash模式
let mode = options.mode || 'hash'
// 是否降级处理
this.fallback = mode === 'history' && !supportsPushState && options.fallback !== false
// 进行降级处理
if (this.fallback) {
mode = 'hash'
}
if (!inBrowser) {
mode = 'abstract'
}
this.mode = mode
// 根据不同的mode进行不同的处理
switch (mode) {
case 'history':
this.history = new HTML5History(this, options.base)
break
case 'hash':
this.history = new HashHistory(this, options.base, this.fallback)
break
case 'abstract':
this.history = new AbstractHistory(this, options.base)
break
default:
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
assert(false, `invalid mode: ${mode}`)
}
}
}
我们可以看到,会判断是否支持 history , 然后根据 fallback 来确定是否要降级。然后,根据不同的 mode , 分别实例化不同的 history 。 (HTML5History、HashHistory、AbstractHistory)
history
我们看到 , HTML5History、HashHistory、AbstractHistory都是来自 history 目录。
├── history // 操作浏览器记录的一系列内容
│ ├── abstract.js // 非浏览器的history
│ ├── base.js // 基本的history
│ ├── hash.js // hash模式的history
│ └── html5.js // html5模式的history
其中, base.js 里面定义了 History 类
基本的关系如下图:
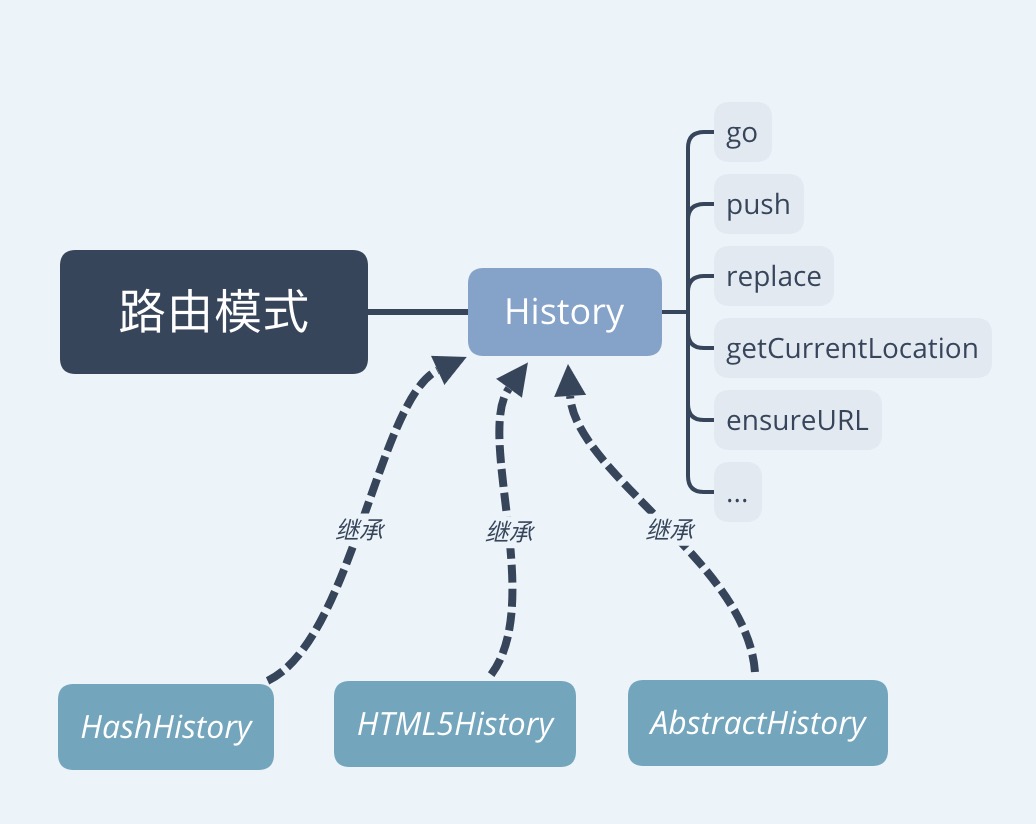
base.js 里面定义了一些列的方法, hash 、html5 模式,分别继承了这些方法,并实现了自己特有的逻辑
从外部调用的时候,会直接调用到 this.history , 然后,由于初始化对象的不同,而进行不同的操作。
接下来, 我们挑选其中一个我们最常用到的 push 方法来解释一整个过程
push 方法
我们平时调用的时候, 一直都是用 this.$router.push('home') , 这种形式调用。
首先,在 VueRouter 对象上有一个 push 方法 。
// 文件位置: src/index.js
export default class VueRouter {
// ... more
push(location: RawLocation, onComplete?: Function, onAbort?: Function) {
this.history.push(location, onComplete, onAbort);
}
}
我们看到,其没有做任何处理,直接转发到 this.history.push(location, onComplete, onAbort)。
上面我们讲到,这个处理,会根据 history 的初始化对象不同而做不同处理。我们来分别看看细节
mode === hash
export class HashHistory extends History {
// ...more
// 跳转到
push(location: RawLocation, onComplete?: Function, onAbort?: Function) {
const { current: fromRoute } = this;
this.transitionTo(
location,
route => {
pushHash(route.fullPath);
handleScroll(this.router, route, fromRoute, false);
onComplete && onComplete(route);
},
onAbort
);
}
}
// 切换路由
// 会判断是否支持pushState ,支持则使用pushState,否则切换hash
function pushHash(path) {
if (supportsPushState) {
pushState(getUrl(path));
} else {
window.location.hash = path;
}
}
mode === history
export class HTML5History extends History {
// ...more
// 增加 hash
push(location: RawLocation, onComplete?: Function, onAbort?: Function) {
const { current: fromRoute } = this;
this.transitionTo(
location,
route => {
pushState(cleanPath(this.base + route.fullPath));
handleScroll(this.router, route, fromRoute, false);
onComplete && onComplete(route);
},
onAbort
);
}
}
两种模式的 push 实现区别并不大,都是调用了 transitionTo , 区别在于: 一个调用 pushHash , 一个调用 pushState.
其他的 go 、 replace 、getCurrentLocation 都是类似的实现方式。
TIP
transitionTo的具体实现,这里就先不详聊了,后面聊到路由守护的时候,会细讲这一块内容。